The Negative Effects of Social Media Addiction on Physical Health
Prior to the birth of Facebook in February 2004, if you wanted a proper catch-up with a friend or family member, you had to arrange to physically meet them...
Negative physical effects of social media
I’ve already posted quite extensively about the negative effects of social media generally, especially on teens and young people, as well as written a number of blogs on the subject. The negative emotional and psychological effects of social media are well covered on the internet. But what’s not so well appreciated are the negative effects it can have on physical health. In the case of adolescents those effects can quite commonly include self-harm and suicide (also see later).
Obesity
According to Cancer Research UK children who spend more than half an hour a day online are 79% more likely to be overweight or obese. The research stated those who are online between 30 minutes and three hours a day are 53% more likely to be carrying excess weight than those who were online for less. This is of concern because social media itself is deliberately designed to be addictive. All the stats indicate that a young person with plenty of friends is likely to be both fitter and happier if they stay off social media altogether and meet their friends in person.
Benefits of being active
Meeting friends in person means you must be at least somewhat physically active and being active has all kinds of benefits. For example, you could walk, run, ride a bike or skateboard to meet your friends. Even if you catch a bus to your meeting, it’s likely you’ll need to walk to the bus stop and then from the bus to your meeting. When you exercise, it increases endorphins, dopamine, adrenaline and endocannabinoid — these are all brain chemicals associated with feeling happy, confident, capable, less anxious and stress-free – even feeling less physical pain.
Exercise is also shown to help some people fight depression, which experts say could be to due an increase in nerve cell growth in the brain that happens when you exercise. Another chemical that is shown to help relieve stress and boost happiness is myokine, which your body creates when your muscles contract as in exercise. According to health experts, these myokines begin to change the function and structure of your brain in ways that make you more resilient to stress and can help people recover from depression and even anxiety disorders.
“Friendships: Enrich your life and improve your health”
That’s according to the Mayo Clinic in the US. It employs over 4,500 physicians and 58,400 administrative and allied health staff across three major campuses. This clinic has ranked number one in the United States for six consecutive years in U.S. News & World Report’s Best Hospitals Honour Roll, maintaining a position at or near the top for more than 35 years.
Physical effects of excessive social media use
According to Dr David Lee, Assistant Professor at the University of Buffalo, research participants who used social media excessively were found to have higher levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a biological marker of chronic inflammation that predicts serious illnesses, such as diabetes, certain cancers, and cardiovascular disease. In addition to elevated CRP levels, results suggest higher social media use was also related to somatic symptoms, like headaches, chest and back pains, and more frequent visits to doctors and health centres for the treatment of illness.
Cyberbullying is on the rise worldwide
One of the risks of being online via social media is Cyberbullying. Pro-consumer website Comparitech gathered both local (US) and global cyberbullying statistics, trends, and facts that help illustrate the extent of this growing problem. The main place Cyberbullying occurs is on social media.
In a survey of 1000 parents with children over the age of 5, sixty percent of parents with children aged 14 to 18 reported them being bullied in 2019.
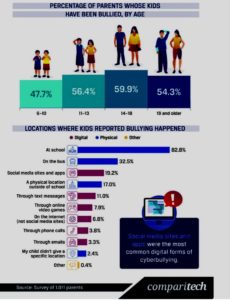
Unfortunately, the most lasting physical effect of cyberbullying is depression, sometimes followed by death. There’s substantial evidence that the internet and social media can influence suicide-related behaviour. Such evidence includes an increase of exposure to graphic content as well as the opportunity for cyberbullying to occur. Over the past ten years, cyberbullying has increasingly led to self-harm and suicide.
In the US, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveal that suicide is the second leading cause of death of US citizens aged 10-14 and 25–34. Although this study does not directly state the cause of these suicides, it can be alluded that cyberbullying was at least a potential cause. Also, the National Center for Health Statistics had previously done a study in 2018 showing that adolescents under the age of 25 that were victims of cyberbullying became twice as likely to commit suicide or to perpetrate various forms of self-harm. Overall, teen suicide rates have increased within the past decade. This is a highly considerable public health problem, with over 40,000 suicide deaths in the United States and nearly one million suicide deaths worldwide occurring annually.
The importance of physically meeting people
Children today are growing up surrounded by mobile devices and interactive social networking sites such as Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and TikTok that have made social media a vital aspect of their lives. Social networking is transforming the behaviour of young people in the manner in which they relate to their parents and peers, as well as how they make use of technology.
Before the invention of social media people had little ability to meaningfully communicate with each other unless that person or people were close by. This is important because when people meet in person, much more goes on than occurs in virtual meetings. For a start, when people meet in person, they very often touch one another. This can be a simple handshake or just someone physically and deliberately touching your arm to display friendship. As researchers at the University of Chicago and Harvard found, touch builds trust. When people shake hands, they are literally activating parts of the brain associated with rewards and conveying warmth to each other.
Friends make good medicine
Lisa Berkman is an American epidemiologist and currently the Thomas D. Cabot Professor of Public Policy, Epidemiology, and Global Health at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. In her paper: Assessing the Physical Health Effects of Social Networks and Social Support she reminds us of the potential and pervasive truth of a notice born on some California shopping bags that “Friends make good medicine”. The message being that social support, (i.e., friendship) is “both good preventive and curative medicine”.
Benefits of face-to-face communication
Here are 5 main reasons why we still need face-to-face meetings and face-to-face communication:
1. Face to face meetings are important for building strong relationships
2. Face to face meetings are important for loyalty and trust
3. Face to face meetings are more focused and productive
4. Face to face meetings clearly communicate goals
5. Face to face meetings helps make focusing easier
